Flexural Strength of Concrete - Applications and Problems

Flexural strength is one measure of the tensile strength of concrete. It is a measure of an unreinforced concrete beam or slab to resist failure in bending. It is measured by loading 6 x 6 inch (150 x 150-mm) concrete beams with a span length at least three times the depth. The flexural strength is expressed as Modulus of Rupture (MR) in psi (MPa) and is determined by standard test methods ASTM C 78 (third-point loading) or ASTM C 293 (center-point loading).
Flexural Strength of Concrete Flexural MR is about 10 to 20 percent of compressive strength depending on the type, size and volume of coarse aggregate used. However, the best correlation for specific materials is obtained by laboratory tests for given materials and mix design. The MR determined by third-point loading is lower than the MR determined by center-point loading, sometimes by as much as 15%.
WHY Test Flexural Strength of Concrete?
Designers of pavements use a theory based onflexural strength. Therefore, laboratory mix design based on flexural strength tests may be required, or a cementitious material content may be selected from past experience to obtain the needed design MR. Some also use MR for field control and acceptance of pavements. Very few use flexural testing for structural concrete. Agencies not using flexural strength for field control generally find the use of compressive strength convenient and reliable to judge the quality of the concrete as delivered.
How to Use Flexural Strength?
Beam specimens must be properly made in the field. Pavement concrete mixtures are stiff (1/2 to 21/2-inch slump). Consolidate by vibration in accordance with ASTM C 31 and tap sides to release air pockets. For higher slump, after rodding, tap the molds to release air pockets and spade along the sides to consolidate. Never allow the beam surfaces to dry at any time. Immerse in saturated lime water for at least 20 hours before testing.
Specifications and investigation of apparent low strengths should take into account the higher variability of 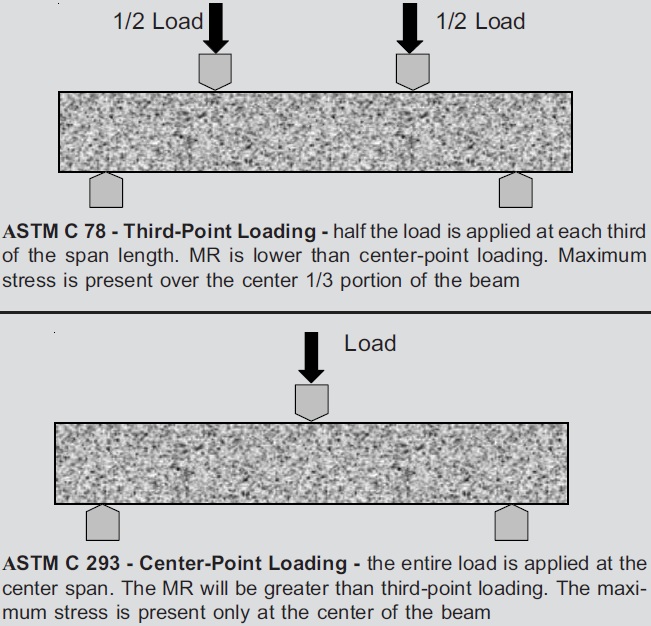 flexural strength results. Standard deviation for concrete flexural strengths up to 800 psi (5.5 MPa) for projects with good control range from about 40 to 80 psi (0.3 to 0.6 MPa). Standard deviation values over 100 psi (0.7 MPa) may indicate testing problems. There is a high likelihood that testing problems, or moisture differences within a beam caused from premature drying, will cause low strength. Where a correlation between flexural and compressive strength has been established in the laboratory, core strengths by ASTM C 42 can be used for compressive strength to check against the desired value using the ACI 318 criteria of 85 percent of specified strength for the average of three cores. It is impractical to saw beams from a slab for flexural testing. Sawing beams will greatly reduce measured flexural strength and should not be done. In some instances, splitting tensile strength of cores by ASTM C 496 is used, but experience is limited on how to apply the data.
flexural strength results. Standard deviation for concrete flexural strengths up to 800 psi (5.5 MPa) for projects with good control range from about 40 to 80 psi (0.3 to 0.6 MPa). Standard deviation values over 100 psi (0.7 MPa) may indicate testing problems. There is a high likelihood that testing problems, or moisture differences within a beam caused from premature drying, will cause low strength. Where a correlation between flexural and compressive strength has been established in the laboratory, core strengths by ASTM C 42 can be used for compressive strength to check against the desired value using the ACI 318 criteria of 85 percent of specified strength for the average of three cores. It is impractical to saw beams from a slab for flexural testing. Sawing beams will greatly reduce measured flexural strength and should not be done. In some instances, splitting tensile strength of cores by ASTM C 496 is used, but experience is limited on how to apply the data.
Another procedure for in-place strength investigation uses compressive strength of cores calibrated by comparison with acceptable placements in proximity to the concrete in question:
What are the Problems with Flexure?
Flexural tests are extremely sensitive to specimen preparation, handling, and curing procedure. Beams are very heavy and can be damaged when handled and transported from the jobsite to the lab. Allowing a beam to dry will yield lower strengths. Beams must be cured in a standard manner, and tested while wet. Meeting all these requirements on a job site is extremely difficult often resulting in unreliable and generally low MR values. A short period of drying can produce a sharp drop in flexural strength. Many state highway agencies have used flexural strength but are now changing to compressive strength or maturity concepts for job control and quality assurance of concrete paving. Cylinder compressive strengths are also The data point to a need for a review of current testing procedures. They suggest also that, while the flexural strength test is a useful tool in research and in laboratory evaluation of concrete ingredients and proportions, it is too sensitive to testing variations to be usable as a basis for the acceptance or rejection of concrete in the field.
Related Pages
References for Flexural Strength of Concrete
- How Should Strength be Measured for Concrete Paving? Richard C.Meininger, NRMCA TIL 420, and Data Summary, NRMCA TIL 451, NRMCA, Silver Spring, MD.
- Concrete Strength Testing, Peggy Carrasquillo, Chapter 14, ASTM STP 169C, Significance of Tests and Properties of Concrete and Concrete-Making Materials, American Society for Testing and Materials, West Conshohocken, PA.











