What is Right of Way - Definition & Factors Affecting RoW
Right of Way Definition
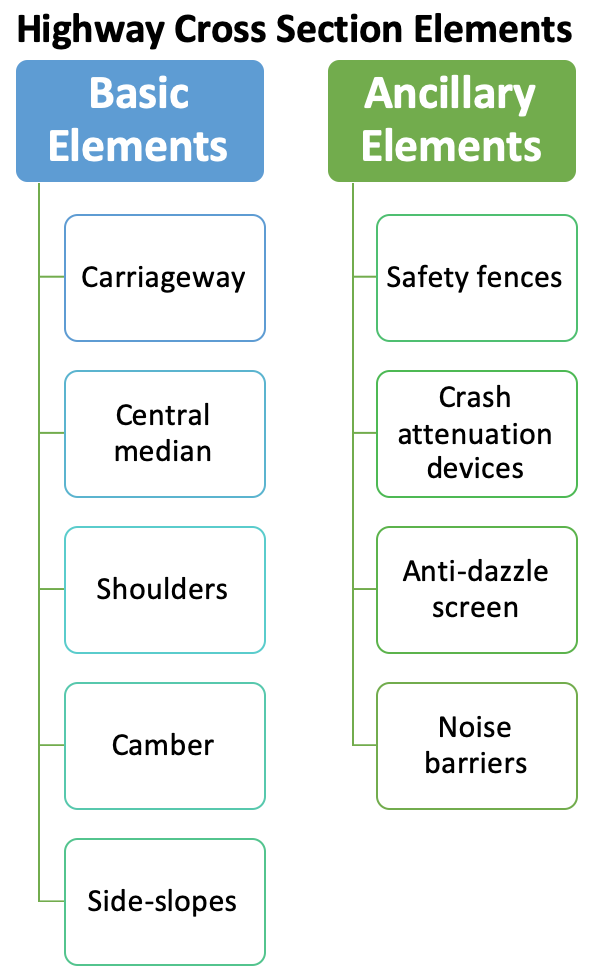
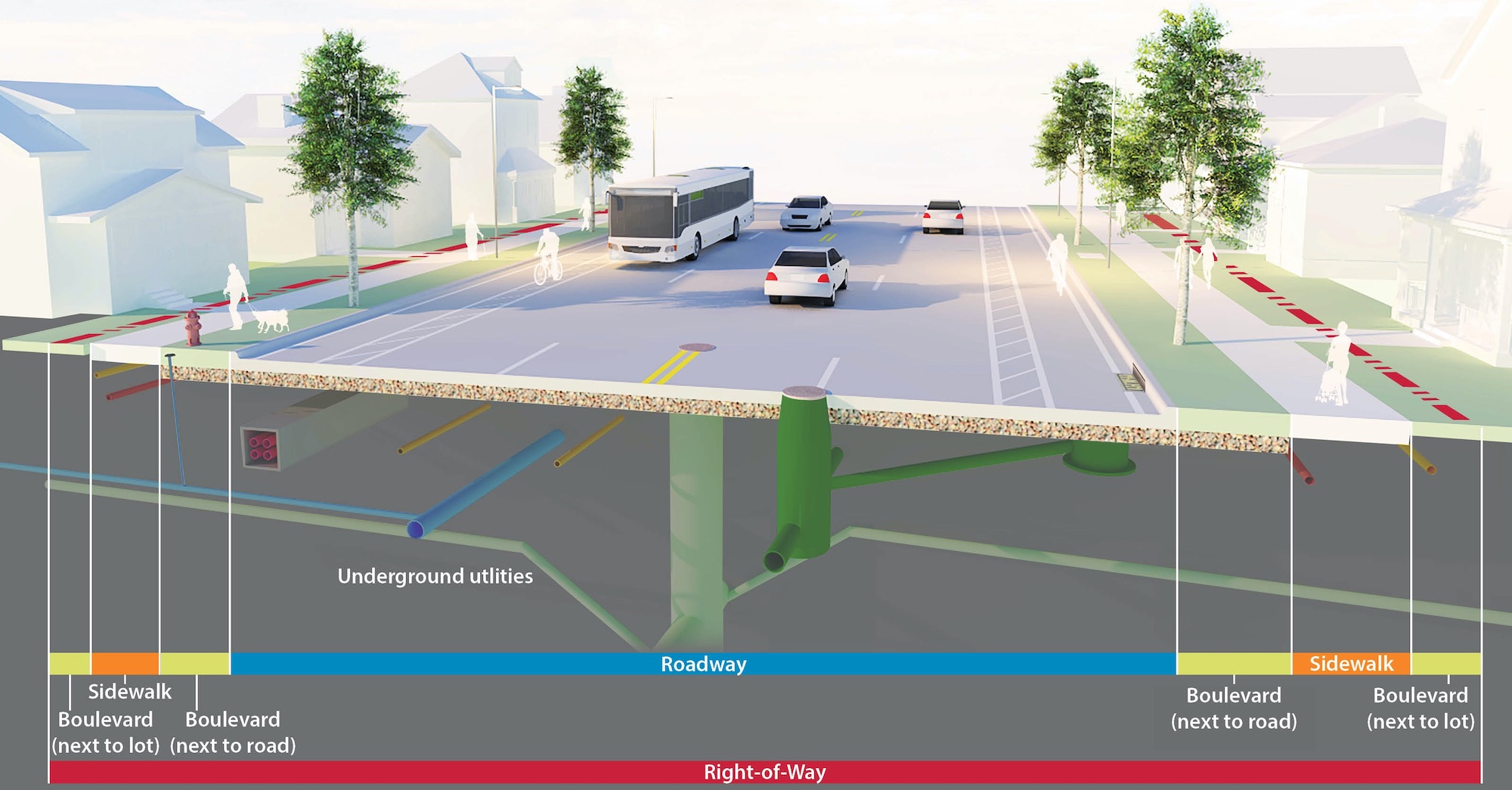
The right of way is the total land area acquired for the construction of the roadway. Its width should be enough to accommodate all the elements of the roadway cross section, any future widening of the road and any public utility facilities that will be installed along the roadway. RoW is the area of the road acquired for carriages way + other necessities + future extension, along its alignment. Good practice is to acquire RoW wide enough to accommodate the ultimate development and all components of the road.
Generally, in India 45 m ROW is acquired for construction of 4-lane road. A typical residential street has a right-of-way width of approximately 60 feet. A typical arterial or downtown street has a right-of-way width of approximately 80 feet. Other widths are less common but not unusual. Alley configurations can vary from 10 feet to 20 feet, but are most commonly 14 feet.
Factors Affecting Right of Way
- Width of formation
- Height of embankment
- Side slopes
- Drainage system
- Sight distances consideration on horizontal curves
- Future extension
Width of Right of Way
Width of RoW according to AASHTO is:
For two lane highway secondary roads AADT 400 – 1000
Min = 66’ ==> Desirable = 80’
Interstate highway system
From 150’ without frontage roads
From 250’ with frontage roads
Up to 200’ – 300’ for eight lane divided highway without frontage roads.
On high type two lane highway in rural area.
Min = 100’ ==> Desirable = 120’
For urban areas acquisition be wide enough to be adequate for ultimate design (no specified width)
Right of Way Video