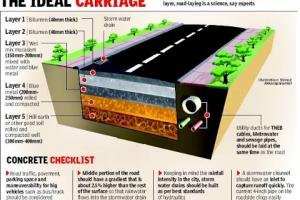
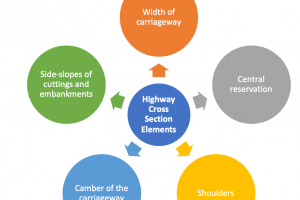
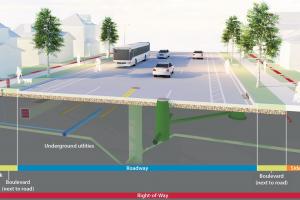
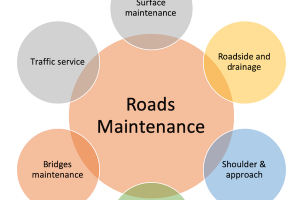
5 Major Classes of Roads - Trunk, Primary, District, Local, Residential

Classes of Roads
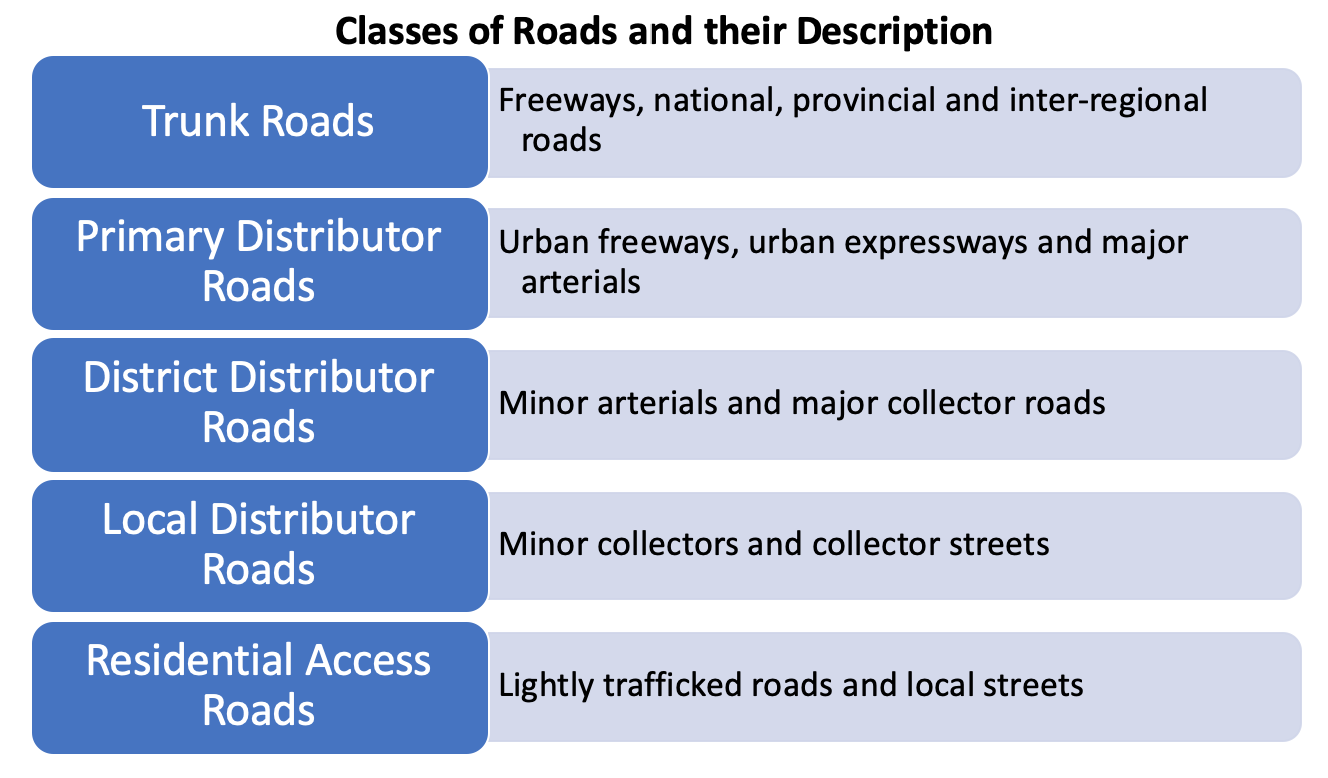
Following are the major classes of Roads:
- Trunk Roads
- Primary Distributor Roads
- District Distributor Roads
- Local Distributor Roads
- Residential Access Roads
Trunk roads:
The main function of this class of roads is to facilitate regional distribution of traffic (intercity movement). They may be national or provincial roads and the type of facilities found in this class are freeways, expressways, dual carriageways and single carriageway main roads, national, provincial and inter-regional roads.
Also See: Types of Roads
Primary distributors:
This class of road forms the primary network for the urban area as a whole. All long distance traffic movements to, from and within the city should be focused onto such roads. Characteristics are high volumes, restricted access and fairly high speeds. Continuity of route is important. Examples of this class of roads are Urban freeways, urban expressways and major arterials.
District Distributors:
Class 3 roads distribute traffic between the various residential, industrial and principal business districts of the town and form the link between the primary network and the roads within residential areas. Examples include Minor arterials and major collector roads.
Local Distributors:
Local distributors are "local" through-roads which distribute traffic within communities and link district distributors. Local bus services are routed along this class of road. The local distributor should carry traffic from a housing module of more than 400 and up to about 1 500 dwelling units. For example Minor collectors and collector streets.
Residential Access Roads:
Residential access roads give people direct access to buildings and land within environmental areas. Access for motor vehicles is not their only function. They are used by the inhabitants for other work, or leisure-time activities such as walking, jogging and playing, as well as for the provision and maintenance of services to houses. Examples of this include Lightly trafficked roads and local streets.