Road Maintenance - Highway Maintenance
Definition of Road Maintenance:
Preserving and keeping each type of roadway, roadside, structures as nearly as possible in its original condition as constructed or as subsequently improved and the operation of highway facilities and services to provide satisfactory and safe transportation, is called Road Maintenance or maintenance of highways.
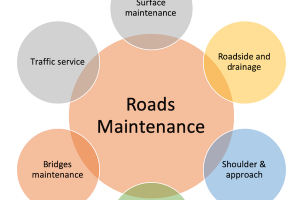
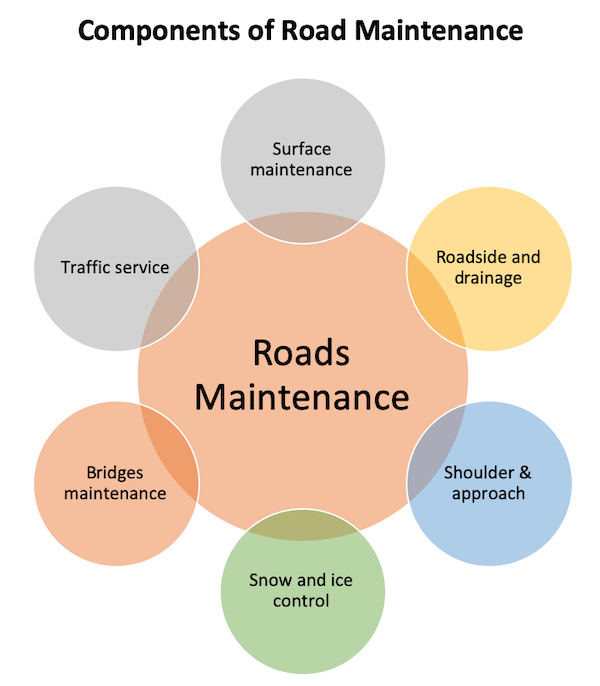
Road Maintenance Components
The various road maintenance function includes:
- Surface maintenance
- Roadside and drainage maintenance
- Shoulder and approaches maintenance
- Snow and ice control
- Bridges maintenance
- Traffic service
Highway maintenance is closely related to the quality of construction of original road. Insufficient pavement or base thickness or improper construction of these elements soon results in expensive patching or surface repair. Shoulder care becomes a serious problem where narrow lanes force heavy vehicle to travel with one set of wheels off the pavement.
Insufficient pavement or base thickness or improper construction of these elements soon results in expensive patching or surface repair. Shoulder care becomes a serious problem where narrow lanes force heavy vehicle to travel with one set of wheels off the pavement.
Improperly designed drainage facilities, mean erosion or deposition of material and costly cleaning operation or other corrective measures. For regular highways maintenance and repair sharp ditches and steep slopes require manual maintenance as compare to cheap repair of flatter ditch and soil by machine.
In snowy country, improper location extremely low fills and narrow cuts leave no room for snow storage, creating extremely difficult snow removal problems.
Also See: Types of Highway Maintenance | Types of Roads
1. Surface Maintenance of Roads
Pavement maintenance and rehabilitation programs restore the riding quality and maintain the structural integrity of the pavement over its full design life. Asphalt concrete pavements are subjected to various types of pavement distress or Failure these include:
a. Surface Distresses
i. Alligator Cracking:
A series of interconnecting or interlaced cracks caused by fatigue of the asphalt concrete surface under repeated traffic leading. [Cracking is due to foundation movement at subgrade]
ii. Block Cracking:
Cracks forming large interconnected polygon usually with sharp corners or angles. These cracks are generated by hardening or shrinking e.g. asphalt or reflection cracking for underlying layers such as cement treated base.
iii. Transverse Cracking:
Cracks approximately at right angle to the pavement center line. These may be caused by hardness and shrinkage of asphalt or differential thermal stresses of asphalt concrete or may be reflection cracking.
iv. Longitudinal Cracking:
Cracks approximately parallel to the pavement center line. These are caused by poorly constructed construction joints and shrinkage of the asphalt concrete surface. Longitudinal cracks may also be reflection cracks.
v. Raveling:
Wearing away the pavement surface caused by dislodging of aggregate particles and binders. This is usually a result of insufficient asphalt binder in the mix or stripping of asphalt from particles of aggregate.
vi. Drip Track Raveling:
Progressive disintegration of the surface between wheel paths caused by dripping of gasoline oil from vehicle.
vii. Bleeding or Flushing (Fatting Up):
The exuding of bitumen on to the pavement surface causing reduction in skid resistance. Bleeding is generally caused by excessive amount of asphalt in the mix or low air void content. It occurs in the mix in hot weather.
viii. Corrugations:
Due to instability of base or poor original riding surface (plastic movement of pavement)
ix. Pot Holes:
When cracks become deep, road surface material comes off becoming small bowl like ditches. These are very important to repair in road maintenance as they cause damage to vehicles and bikes.
x. Ruts:
Depressions formed under the wheel due to heavy load, this causes consolidation, deformation or plastic flow.
b. Methods of Surface Treatment for Road Maintenance
The surface treatment may be single or multiple. Although the best type of surface course is pre-mix carpet for roads maintenance. The surface treatment methods are employed when:
- Intensity of traffic is not very high.
- the pro-mix mixers are not easily available due to long transportation or technical reasons.
- when the cost is high.
In Highway Maintenance, for good surface treatment it is necessary that:
- Base course is well prepared to its profile and is made more free from pot holes and ruts.
- Excellence of surface dressing depends upon the correct proportion of binder aggregate.
- Before laying that first surface dressing coat, the base should be made free from all dust loose soil etc.
In all bituminous construction it is necessary that the newly surface posses a bond with the existing base at the interface. It is also necessary that the base is nearly impervious.
- For maintenance of gravel roads blading and occasional resurfacing is required.
- For surface treatments of low type bituminous surface in maintenance of roads; Patching, seal coating or possible loosening oiling, re mixing and relaying are involved.
- For high type bituminous concrete and Portland cement concrete, the Removal and replacement of failure areas and resurfacing are approximate treatment methods for highway maintenance.
- Use same material and methods for road surface maintenance as far as possible.
- Maintenance and repairs of roads must be planned for rapid performance and to cause least possible disruption or hazard to traffic.
2. Roadside and Highway Drainage maintenance
Depends on the characters of road side where the roadside is grassy it must be mowed; cutting, ploughing or spraying with weed killer must be done.
If there is dry grass fire hazard burning, plowing must be done in road maintenance. To improve visibility and increase the sight distance and clearance of road trimming should also be done. Its important to note that side slope erosion by mulching, seeding etc should be checked and controlled as and where required to ensure slope and shoulder stability. Furthermore, picking up litter, thrown or blown along roadside or wayside area should be a routine work.
Drainage of Highways: Keeping ditch, culvert and other drainage structure, clean and ready to carry next flow water. Sediments deposited during period of heavy flow must be removed badly eroded channel and dikes properly protected to prevent recurrence.
3. Shoulders Maintenance:
The maintenance of shoulders depend on the surface character of the area where the maintenance and repair is performed.
SOD shoulders (Sod shoulders are earth shoulders on which a solid turf has been established. Normally they require very little maintenance and holes, ruts, and settlements should be repaired with sod or stabilized material.) must be moved and occasionally bladed down to the level of the roadway so that water is not trapped in the traveled way. Grass must be kept in good condition. In maintenance of roads shoulders protected by bituminous blankets have surface treatments same as for roadway surface.
Gravel and earth shoulders that leaves a drop off at the pavement edges creates a serious accident hazard, hence, should be corrected by reconstruction, resurfacing or other appropriate means. Due to continuous wetting and drying of shoulder, edge joints result between lane and shoulder which may cause settlement of pavement due to entrance of water in sub grade soil. It can Repaired by filling the joint with sand and asphalt concrete
4. Snow and ice control:
Ice forming on the roadway reduces coefficient of friction between tires and surface, which makes vehicle control almost impossible. In repair of roads, we can apply abrasive to heavily traveled roadway and street. Suitable materials that can be used are clean and sharp sand, cinders and washed stone screening.
5. Bridge maintenance:
 Bridges maintenance is a major part of roads maintenance. Bridges can be maintained in good condition by following the below guidelines:
Bridges maintenance is a major part of roads maintenance. Bridges can be maintained in good condition by following the below guidelines:
- Exposed steel work must be cleaned by sand blasting flame or other means followed by repainting.
- Deck joint may extrude or become filled with dirt so that cleaning and resealing is necessary.
- Out of control vehicle, causing damage to guard rail, must be repaired and strengthened.
- If bridge deck become rough resurfacing is required
- Remedial measures to correct serious scour around and under piers and abutments.
6. Traffic services:
Include stripping, sign repair and maintenance (particularly needed for repair after stormy weather).
Factor Affecting Roads Maintenance:
Generally following factors affect the maintenance of pavements:
Increase in the intensity of traffic.
Since we know that there is increase in road transport per year about 8%. Hence this is the most important factor, which affects the maintenance of roads.
Inadequate Thickness of Pavement.
As already discussed adequate thickness of pavement is essential. If the adequate thickness is not provided, it will result frequent pavement failure, unevenness and heavy patches.
Effect on No of lanes.
The road research laboratory has established by experiments that concentration of road is almost 4 times larger on a single lane pavement than a double lane pavement section. Thus the road distress and maintenance on single lane pavement are higher than double lane pavements.