Types of Precipitation Based on Lifting Mechanism
Although moisture is always present in the atmosphere but it is condensed only when air is cooled and saturated with some water vapors. Usually mechanism by which air is cooled to cause precipitation is the lifting of air mass. Precipitation is often classified according to the factor responsible for lifting of air to higher altitudes. Following are the various types of precipitation based on this classification.
- Convectional Precipitation
- Orographic Precipitation
- Cyclonic Precipitation
Convectional Precipitation
Definition
 It is due to the upward movement of warm air. Generally this type of precipitation occurs in tropical region, where in hot days, the ground surface is heated unequally, and causing the warmer air to lift up as the colder air comes to take its place. The vertical air currents develop tremendous velocities and are dangerous for aircrafts.
It is due to the upward movement of warm air. Generally this type of precipitation occurs in tropical region, where in hot days, the ground surface is heated unequally, and causing the warmer air to lift up as the colder air comes to take its place. The vertical air currents develop tremendous velocities and are dangerous for aircrafts.
The main cause of Convectional precipitation is thermal convection of the moisture laden air (rising of warmer, lighter air in colder, denser surroundings).
What causes Convectional Precipitation
- A major portion of the solar radiation is utilized in heating the earth. As the earth conducts heat slowly, the heat accumulates at the surface of the earth and air which comes in its contact is heated up and the lapse rate near the surface of the earth increases rapidly. With the passage of time as the sun gets higher and higher the lapse rate increases further and air becomes unstable.
- Vertical currents are then set up which carry heat and the moisture laden air is picked up from the surface to higher levels. Due to convection, the moist air in the lower levels of the atmosphere rises up to the condensation level where clouds develop and with further convection these clouds finally grow resulting in a thunderstorm.
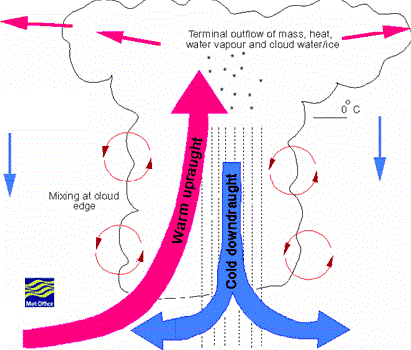
Characteristics of Convectional Precipitation
- Precipitation occurs in the form of showers of high intensities and short duration،
- In summer most parts of Pakistan gets this type of precipitation.
Orographic Precipitation
Definition
This type of precipitation is caused by air masses striling some natural topographic barriers like mountains. As it cannot move forward it rises up causing condensation and precipitation.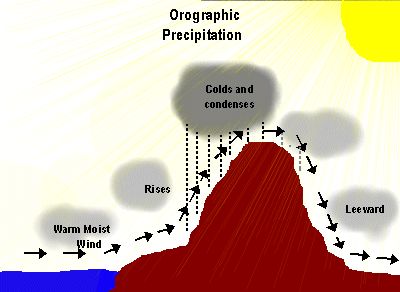
Causes of Orographic Precipitation
- In the orographic precipitation, expansion and condensation occurs because moisture laden air masses are lifted by contact with orographic (mountain) barriers.
Characteristics of Orographic Precipitation
- This type of precipitation is most pronounced on the windward side of mountain range, generally heaviest precipitation occurs where favorable orographic effects are present.
 Orographic precipitation also occurs in the inland areas where mountain ranges rise above the surrounding areas in the path of the moisture laden air masses.
Orographic precipitation also occurs in the inland areas where mountain ranges rise above the surrounding areas in the path of the moisture laden air masses.- The greater amount of precipitation falls on the windward side.
- Orographic barriers tend to increase both cyclones and orographic precipitation because of the lifting of air.
- Rainfall is composed of steady rainfall.
- Southern slope of the Himalayas is a good example of this kind.
- Similarly, winds coming from ocean strike the western slopes of coastal ranges causing heavy rains.
- All three types of precipitations occur due to lifting of air.
Cyclonic precipitation
Definition
Cyclone is a type of atmospheric disturbance by mass of air circulating clockwise in southern and anticlockwise in northern hemispheres.
- Precipitation in plain regions is generally cyclonic in character.
- Cyclonic precipitation results from the lifting of air converging into a low-pressure area or cyclone.
- Cyclonic precipitation can be frontal or non-frontal.
 Frontal precipitation results from the lifting of warm air on one side over a colder denser air on the other side.
Frontal precipitation results from the lifting of warm air on one side over a colder denser air on the other side.- Warm-front precipitation is formed in the warm air advancing upward over a cold air mass.
- Cold-front precipitation is formed in the warm air is forced upward by an advancing mass of cold air
Characteristics of Cyclonic Precipitation
- Cyclone is also a violently rotating wind storm.
- It is a large whirling mass all converging into a low pressure area, air will flow horizontally from surrounding area, causing air in the low pressure area to lift. The precipitation that results is called non-frontal cyclonic precipitation.
- If one air mass passes over another air mass, the precipitation is frontal cyclonic precipitation.
- The air rushes horizontally into the low pressure area changing into whirling mass because of rotary motion of the earth about its own axis. This cyclone is very large mass of air ranging from 800 to 1600km in diameter and moving with a velocity of 50 km/hr.
- The cyclonic precipitation occurs in the form of drizzle, intermediate rain or steady rain.
- Precipitation caused by cold front is intense and of short duration.
- Precipitation caused by warm front is more continuous.
In the Indo-Pak Subcontinent, the cyclonic storms form in the Bay of Bengal in different months. During April, May and June most of these storms do not reach Pakistan. But some of them affect Bangladesh and give very heavy rainfall there. During the summer monsoon season, the cyclonic storms reach Pakistan and are fed with moisture from the Arabian sea resulting in heavy rainfall over the Northern areas of Pakistan. In September, October and November these storms are very destructive in Bangladesh. Such storms cause considerable loss of life and property over the coastal districts. Cyclonic storms also form in Arabian sea but their number is far less.