Dampness in Buildings and DPC (Damp Proof Course)

![]() Types of Floor Lecture Notes
Types of Floor Lecture Notes
Definition:
The access and penetration of moisture content into building through its walls, floor, roof etc. is called dampness in buildings.
Effects of dampness in buildings:
- Causes rotting of wood.
- Causes corrosion of metallic fixtures.
- Deteriorate electric installations.
- Deteriorate carpet & furniture’s.
- Causes spots on the floors and walls.
- Causes petting off and removal of plaster.
- Causes bleaching and blistering of paints.
- Causes efflorescence in bricks, tiles and stones
- Dangerous for the health of occupants.
- Reduces the life of structures
- Promotes growth of termites
Causes of dampness in buildings
- Rain penetration
- Level of site
- Drainability of soil
- Climate condition
- Defective orientation of building
- Moisture entrapped during construction
- Defective construction e.g. joints
- Use of poor quality bricks which ultimately absorb a lot of water.
- Use of Poor quality of concrete (permeable concrete)
Methods of preventing dampness in buildings
- By providing DPC ( Damp proof course )
- By surface treatment i.e. by providing damp proof paint
- By integral water proofing method
- By special devices i.e. by providing chajjas & by providing cavity walls etc
Corbels
This is provided in internal side of roofs
- For decoration
- For preventing dampness
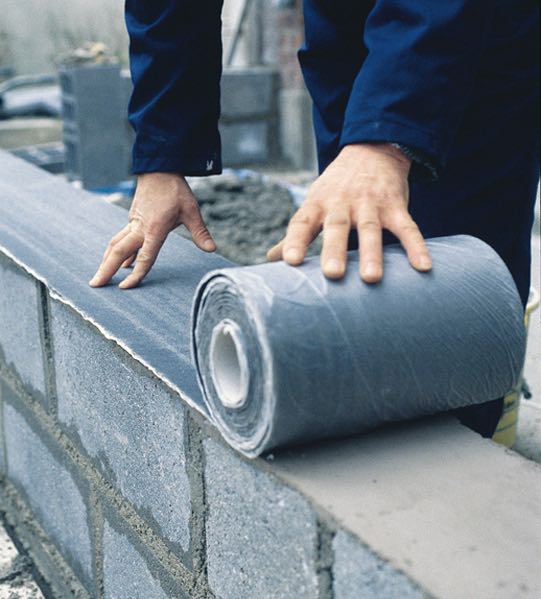
DPC - Damp proof course
It is continuous layer of impervious material applied to prevent moisture transmission. A common example is polyethylene sheeting laid under a concrete slab to prevent the concrete from gaining moisture through capillary action. A DPM may be used for the DPC.
Rising damp is caused by capillary action drawing moisture up through the porous elements of a building's fabric. Rising damp, and some penetrating damp, can be caused by faults to, or the absence of a damp-proof course (DPC) or damp-proof membrane (DPM).
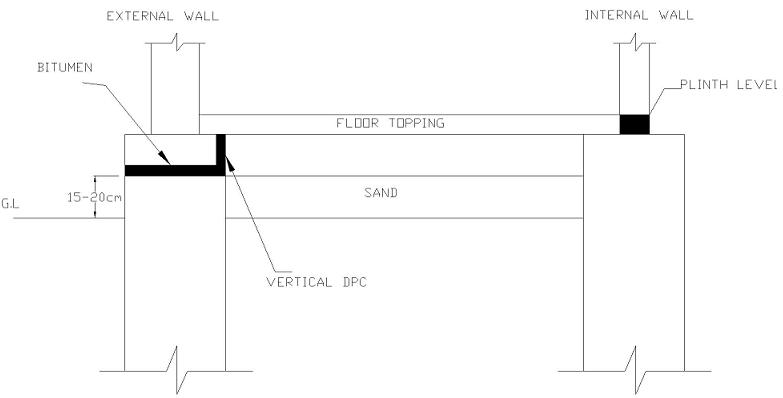
- For internal wall we only provide horizontal DPC ( 175 kg/cm 2 standard pressure for bitumen )
- Three layers of bitumen is provided
- You should provide a mortar layer before DPC
Types of DPC
There are two types of DPC
- Flexible DPC: It is DPC when load doesn’t crack e.g. Polythene and Bitumen
- Rigid DPC: It is DPC when loaded; it cracks e.g. Rich cement concrete 1:2:4
Three layers
- Bitumen mastic: Bitumen mix with fine sand
- Bitumen felt: It is available in the form of rolled sheets
- Hard laid bitumen
- Metal sheets
e.g. Lead, copper, aluminum is provided with mortar, to avoid rusting.
Rigid DPC: It is DPC when loaded; it cracks e.g. Rich cement concrete 1:2:4