Bamboo as Concrete Reinforcement
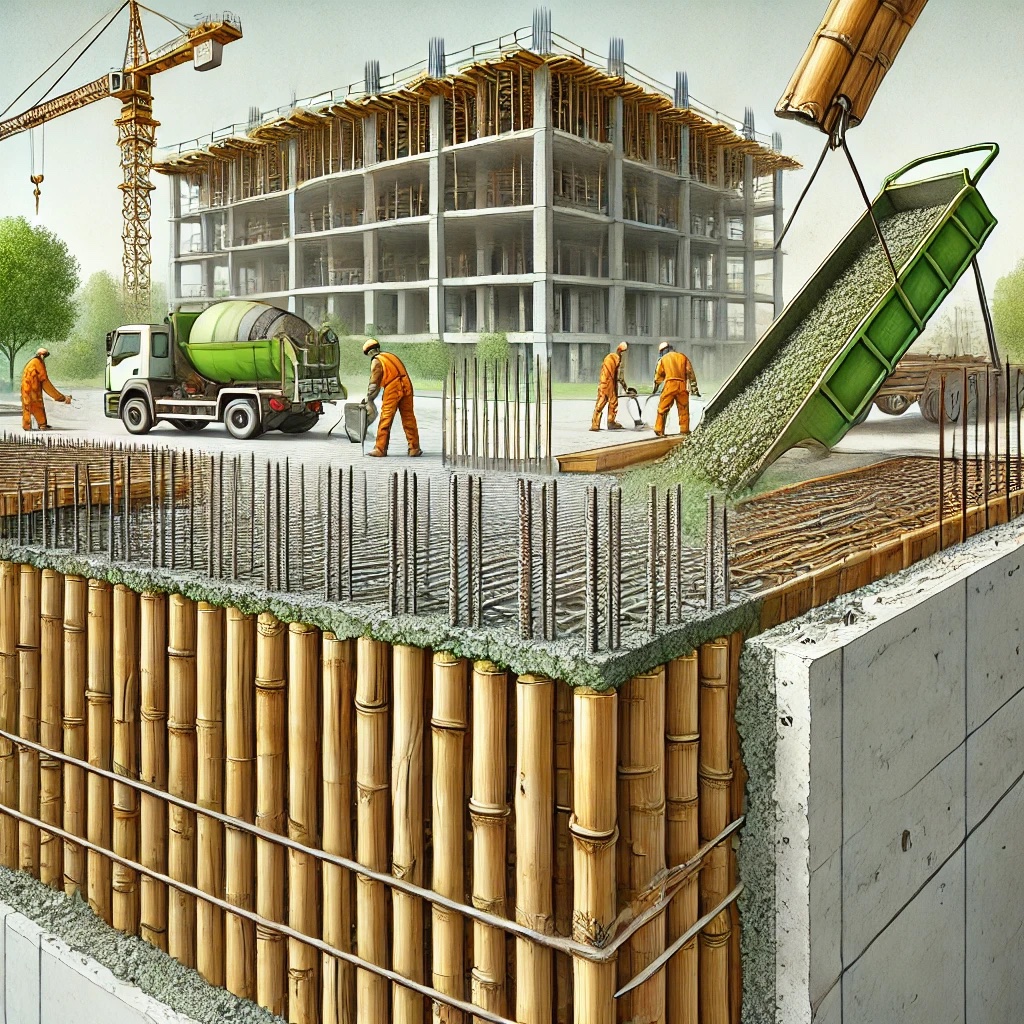

Concrete is the most widely used construction material in the world, often reinforced with steel to enhance its tensile strength. However, steel production is energy-intensive and contributes significantly to carbon emissions. As sustainability becomes a priority in construction, researchers and engineers are exploring bamboo as an eco-friendly alternative to steel reinforcement. Bamboo's high tensile strength, rapid growth rate, and renewability make it a promising material for reinforced concrete structures as well as other uses in Building Construction. Let's discuss using Bamboo as Concrete Reinforcement:
Why Bamboo as Concrete Reinforcement?
1. High Tensile Strength
Bamboo has a tensile strength that rivals steel, making it an excellent material for reinforcing concrete. Its natural fibers provide flexibility and resilience, allowing it to absorb stress and prevent cracking in concrete structures.
2. Sustainability
Unlike steel, which requires significant energy and resources to produce, bamboo is a rapidly renewable resource. It grows quickly, maturing in 3-5 years, and can be harvested without damaging the plant's root system, ensuring continuous regrowth.
3. Cost-Effectiveness
Bamboo is significantly cheaper than steel, especially in regions where it is locally abundant. Its low cost makes it an attractive option for construction projects in developing countries or for budget-conscious builders.
4. Lightweight and Easy to Handle
Bamboo is much lighter than steel, making it easier to transport and handle on construction sites. This reduces labor costs and simplifies the construction process.
5. Low Carbon Footprint
Bamboo absorbs large amounts of carbon dioxide during its growth, making it a carbon-negative material. Using bamboo as reinforcement reduces the overall carbon footprint of construction projects.
Properties of Bamboo as Concrete Reinforcement
1. High Tensile Strength
Bamboo has a tensile strength comparable to mild steel (approximately 100-400 MPa, depending on the species), making it a strong candidate for reinforcing concrete.
2. Lightweight and Flexible
Bamboo is much lighter than steel, reducing the overall weight of the structure and making transportation and handling easier.
3. Sustainability and Renewability
Unlike steel, which requires mining and energy-intensive processing, bamboo grows rapidly (maturing in 3-5 years) and absorbs large amounts of CO₂ during its growth cycle.
4. Natural Durability and Resistance
Treated bamboo can resist environmental factors such as moisture, pests, and decay, enhancing its longevity in concrete structures.
5. Bonding with Concrete
Bamboo’s natural surface is smooth and does not bond well with concrete. To improve adhesion, bamboo is treated with epoxy coatings, sandblasting, or mechanical modifications.
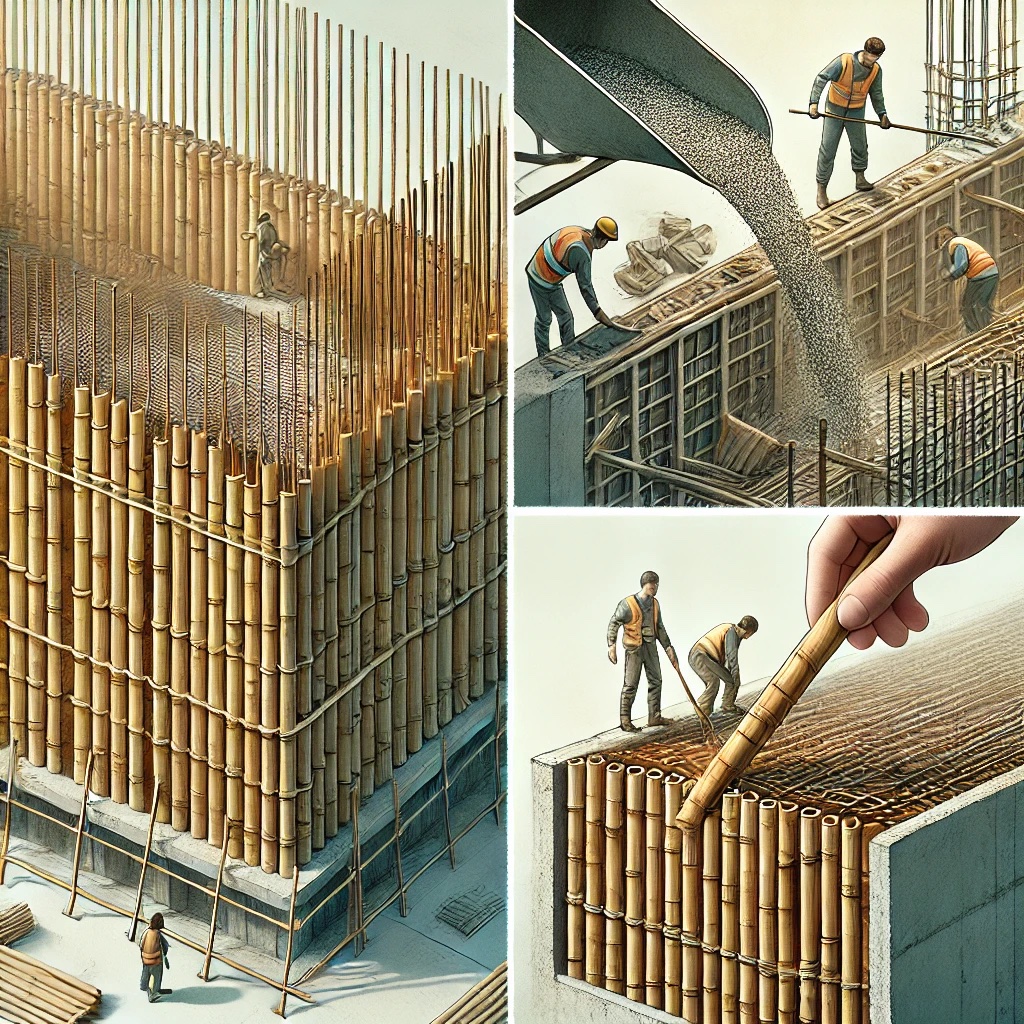

Real-World Applications of Bamboo as Concrete Reinforcement
1. Bamboo-Reinforced Concrete in Colombia
In Colombia, researchers and engineers have experimented with bamboo-reinforced concrete for low-cost housing projects. The use of bamboo as reinforcement has proven effective in creating durable and affordable homes, particularly in rural areas where steel is expensive and difficult to source.
2. Bamboo Reinforcement in India
In India, bamboo has been used as reinforcement in concrete slabs and beams for small-scale infrastructure projects. The Auroville Earth Institute in Tamil Nadu has conducted extensive research on bamboo-reinforced concrete, demonstrating its potential for sustainable construction in earthquake-prone regions.
3. Bamboo-Reinforced Concrete in the Philippines
The Philippines has also embraced bamboo as a reinforcement material for concrete. The country's Department of Science and Technology (DOST) has supported research into bamboo-reinforced concrete for low-cost housing and community infrastructure, showcasing its potential for disaster-resilient construction.
4. Experimental Projects in Germany
In Germany, researchers at the University of Stuttgart have explored the use of bamboo as reinforcement in lightweight concrete structures. Their experiments have shown that bamboo-reinforced concrete can achieve comparable strength to steel-reinforced concrete while significantly reducing the environmental impact.
Challenges and Solutions in Using Bamboo for Reinforcement
- Water Absorption & Swelling: Bamboo absorbs moisture, causing swelling and weakening concrete. Applying water-resistant coatings like epoxy or linseed oil helps mitigate this issue.
- Durability Concerns: Untreated bamboo decomposes over time. Proper chemical treatments (boron or resin-based coatings) can increase its lifespan.
- Bonding Issues: Bamboo’s smooth surface can lead to weak adhesion with concrete. Surface roughening, notching, or epoxy application can improve the bond strength.
- Structural Standards: Unlike steel, bamboo lacks universal standards for reinforcement. Ongoing research is working toward establishing engineering guidelines for bamboo-reinforced concrete structures.
Advantages of Bamboo as Concrete Reinforcement
1. Environmental Benefits
-
Renewable Resource: Bamboo grows quickly and can be harvested sustainably, making it an eco-friendly alternative to steel.
-
Carbon Sequestration: Bamboo absorbs CO2 during its growth, helping to mitigate climate change.
-
Reduced Energy Consumption: The production and processing of bamboo require far less energy than steel.
2. Economic Benefits
-
Low Cost: Bamboo is more affordable than steel, especially in regions where it is locally available.
-
Local Sourcing: Using bamboo reduces transportation costs and supports local economies.
3. Structural Benefits
-
High Tensile Strength: Bamboo's natural fibers provide excellent reinforcement for concrete.
-
Flexibility: Bamboo's flexibility allows it to absorb stress and prevent cracking in concrete structures.
4. Ease of Use
-
Lightweight: Bamboo is easier to handle and transport than steel, reducing labor costs.
-
Workability: Bamboo can be cut, shaped, and installed with simple tools, making it accessible for small-scale construction projects.
Conclusion
Bamboo-reinforced concrete presents a viable, sustainable alternative to steel reinforcement, particularly for low-cost, eco-friendly construction. While challenges such as water absorption and durability need to be addressed, ongoing research and innovative treatment methods are making bamboo an increasingly practical material for reinforcement. As the construction industry shifts toward greener practices, bamboo has the potential to play a significant role in sustainable building solutions.
References
- Ghavami, K. (2005). Bamboo as reinforcement in structural concrete elements. Cement and Concrete Composites, 27(6), 637-649.
- Janssen, J. J. A. (2000). Designing and Building with Bamboo. Technical University Eindhoven.
- Liese, W. (1998). The Structure and Properties of Bamboo in Relation to Its Use as a Building Material. International Journal of Bamboo Research, 2(1), 10-20.
By leveraging bamboo’s unique properties, the construction industry can move toward more sustainable and cost-effective solutions without compromising strength and durability.