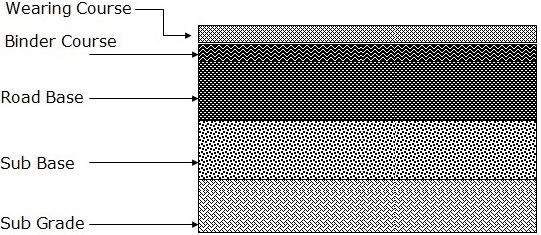
Components of Road Structure | Methods of Construction of Road Structure
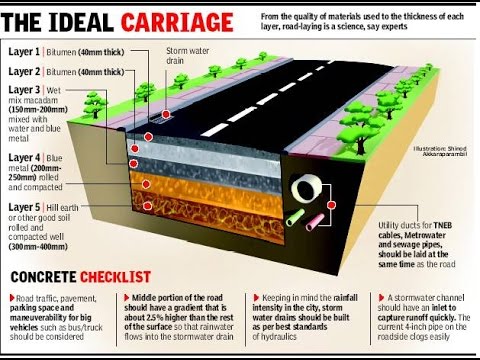
A road structure consists of the following components:
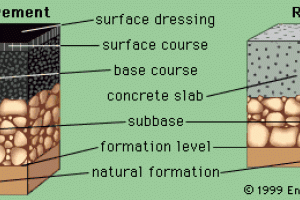
1. Sub Grade:
Subgrade is the foundation of the road, thus its the lowest and most important component of road structure.
Construction:
- If natural surface is above the formation level then the surface is cut down to proposed sub grade surface
- If natural surface is below the formation level then the sub grade will be above the ground level
- It should be constructed at least 60 cm (2ft) high from highest flood level of the area
Function of Sub grade:
-
Bears all the load thus acts as a foundation of road
- Transfer load through grain to grain contact
Material:
Material of sub grade should be strong enough to bear the loads, easily accessible and available in the vicinity and cheap.
2. Sub Base:
Consists of:
- Upper Base Course
- Sub or Lower Base Course
Construction:
- Constructed above the sub grade
- Not needed if the sub grade is of very high strength
- In case of flexible pavement upper and lower base courses are separated having different materials
- In case of rigid pavement only upper base course is provided
- Thickness varies from 7.5 (3in) to 15cm (6in)
Functions of sub base:
- Prevent rise of water or capillary action
Material:
- Should be better than the material of Sub Grade
- The Upper Base Course is made up of sand, gravel, and stone
- The Lower Base Course is made up of cheaply available material i-e rock and stone fragments
3. Road Base:
Due to quality of material used in the road base it is divided into
- Upper Road Base
- Lower Road Base
Construction:
- Constructed above the Sub Base
Functions of Road Base:
- To avoid the distortion of wearing course due to its sufficient density
- Supports the wearing course
Material:
- In case of Upper Road Base the material is of high quality as the load intensity is high
- In case of Lower Road Base the material is of high quality as the load intensity decreases
4. Surfacing:
It is the upper most layer of road cross section. It can be provided in one or two layers:
Construction:
Constructed usually in two layers
- Binder Course
- Wearing Course (It is the layer which is in direct contact with the tyres of the vehicle)
Functions of Surfacing of Road:
- Prevent penetration of water in to the pavement
- Binder Course binds the Wearing Course with the Road Base
- Wearing Course provide a smooth riding
- Saves the lower layers from abrasion and weathering effects of the moving vehicles
Material:
- Made up of bituminous material
- For Flexible Pavement asphalt concrete is used
- For Rigid Pavements Reinforced Cement Concrete (RCC) is used