Coffer Dam - Applications and Working Mechanism
Definition:
A cofferdam can be defined as "A watertight construction designed to facilitate construction projects in areas which are normally submerged", such as bridges and piers.
The multiple-stage method of diversion over the tops of alternate low construction blocks or through diversion conduits in a concrete dam requires shifting of the coffer dam from one side of the river to the other during construction. During the first stage, the flow is restricted to one portion of the stream channel while the dam is constructed to a safe elevation in the remainder of the channel.
In the second stage, the coffer dam is shifted and the stream is carried over low blocks or through diversion conduits in the constructed section of the dam while work proceeds on the un-constructed portion. The dam is then carried to its ultimate height, with diversion finally being made through the spillway, penstock, or permanent outlets.
 A cofferdam is installed in the execution area and the water is pumped out in order to facilitate work for workers and enable them to work in dry conditions and can construct structural supports, enact repairs, or perform other types of work in a dry environment. In some regions of the world, a cofferdam is better known as a caisson. Working inside a cofferdam can be hazardous if it is installed improperly or not safely pressurized, but advances in engineering have led to increased safety for workers using this unique work environment.
A cofferdam is installed in the execution area and the water is pumped out in order to facilitate work for workers and enable them to work in dry conditions and can construct structural supports, enact repairs, or perform other types of work in a dry environment. In some regions of the world, a cofferdam is better known as a caisson. Working inside a cofferdam can be hazardous if it is installed improperly or not safely pressurized, but advances in engineering have led to increased safety for workers using this unique work environment.
A coffer dam is a temporary dam or barrier used to divert a stream or to enclose an area during construction. The design of an adequate cofferdam involves the problem of construction economics. When the construction is timed so that the foundation work can be executed during the low-water season, the use of cofferdams can be held to a minimum. However, where the stream flow characteristics are such that this is not practical, the cofferdam must be so designed that it is not only safe, but also of the optimum height.
Working Mechanism of a Coffer Dam
The working mechanism of a cofferdam involves creating a temporary enclosure or barrier in a water body to allow construction or repair activities to be carried out in a dry or controlled environment. Cofferdams are typically constructed using sheet piles, concrete walls, or other suitable materials. The working mechanism can vary depending on the type of cofferdam used, but here is a general overview of how cofferdams work:
Enclosure: The cofferdam is constructed to enclose the desired area in the water body where construction or repair work needs to be done. The size and shape of the cofferdam are determined based on project requirements and site conditions.
Water Exclusion: The primary function of the cofferdam is to exclude water from the enclosed area, creating a dry or controlled working environment. This is achieved by installing sheet piles or constructing impermeable walls around the perimeter of the cofferdam. The sheet piles or walls are driven or constructed into the ground to form a watertight seal.
Water Pumping: Once the cofferdam is in place, any water inside the enclosed area is pumped out to create a dry working space. Submersible pumps or other dewatering techniques are used to remove the water from the cofferdam. The pumping continues throughout the construction or repair activities to maintain the dry conditions.
Construction or Repair Activities: With the enclosed area now dry or controlled, the intended construction or repair activities can take place. This can include building foundations, installing pipelines, constructing bridges or structures, performing maintenance or inspections, or any other work required.
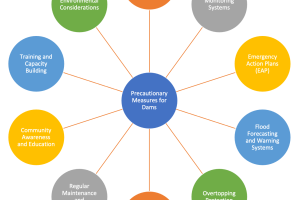
Safety Measures: Safety measures are put in place to ensure the stability and integrity of the cofferdam during the construction process. This may include reinforcing the cofferdam structure, monitoring water levels and pressures, securing the cofferdam against wave action or currents, and implementing proper access and egress systems for workers.
Removal of the Cofferdam: Once the construction or repair work is completed, the cofferdam is dismantled, and the enclosed area is returned to its original state. Any sheet piles or walls used for the cofferdam are extracted, and the water is allowed to flow back into the area.
The working mechanism of a cofferdam is designed to create a temporary dry or controlled environment for construction or repair activities, allowing them to be carried out efficiently and safely in a water body. The specific details of the working mechanism can vary depending on the design, type, and size of the cofferdam, as well as the specific project requirements.
Design of Coffer Dams
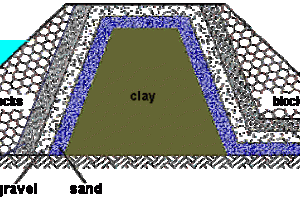
Whose design considerations closely follow those for permanent dams of the same type. Other less common coffer dam types are concrete cribs filled with earth or rock, and cellular-steel cofferdams filled with earth or rock. In this case, the major portion of the cofferdam consists of an earth and rock embankment, and steel sheet piling was used to affect final closure in swift water. Cellular steel cofferdams and steel sheet piling are adaptable to confined areas where currents are swift.
If the coffer dam can be designed so that it is permanent and adds to the structural stability of the dam, it will have a decided economic advantage. In some embankment dams the cofferdam can even be incorporated into the main embankment. In such instances, the saving is twofold-the amount saved by reducing the embankment material required and the amount saved by not having to remove the cofferdam when it is no longer needed.
Applications of Coffer Dams
Cofferdams have a wide range of applications in various industries and construction projects. Some of the common applications of cofferdams include:
Bridge Construction and Repair: Cofferdams are frequently used during the construction and repair of bridges. They create a dry workspace around the bridge piers or abutments, allowing workers to construct or repair the foundation, columns, or other structural elements without being hindered by water. Cofferdams provide a safe and controlled environment for bridge construction and maintenance.
Dam Construction and Maintenance: Cofferdams play a vital role in the construction and maintenance of dams. They are used to create a dry working area within the dam site, allowing for excavation, foundation preparation, concrete pouring, and other construction activities. Cofferdams also facilitate repairs, inspections, and maintenance work on dam structures, gates, or spillways.
Pipeline Installation and Repair: When installing or repairing underwater pipelines, cofferdams are often employed. They create a temporary dry or controlled environment around the pipeline, enabling workers to carry out welding, jointing, or other maintenance tasks. Cofferdams ensure that the pipeline work can be performed efficiently and safely, minimizing the need for costly and time-consuming divers or underwater equipment.
Water Intake Structures: Cofferdams are used in the construction of water intake structures, such as those for water treatment plants, power plants, or irrigation systems. They allow for the construction of intake wells or chambers, screens, gates, or pumping stations. Cofferdams create a dry workspace for workers to install, repair, or maintain water intake infrastructure.
Marine Construction: In marine environments, cofferdams are utilized for various construction projects. They are used for the construction of offshore platforms, jetties, wharves, seawalls, or breakwaters. Cofferdams facilitate the construction of these structures by providing a dry working space and preventing water ingress during the construction process.
Environmental Remediation: Cofferdams can be used for environmental remediation purposes, particularly in areas contaminated with pollutants or hazardous materials. They are employed to isolate and contain the contaminated area, preventing further spreading of pollutants and facilitating cleanup operations. Cofferdams allow for the extraction of contaminated soil or water and the implementation of remediation techniques in a controlled environment.
Underwater Inspections and Repairs: Cofferdams can also be used for underwater inspections and repairs in marine structures, such as ship hulls, offshore platforms, or underwater pipelines. They create a dry working environment around the specific area that needs to be inspected or repaired, enabling workers to carry out the tasks efficiently and effectively.
Overall, cofferdams find application in various construction projects that require a temporary enclosure in water bodies. They provide a controlled, dry working environment, allowing for efficient construction, repair, and maintenance activities while ensuring worker safety and minimizing environmental impact.
Height Limitations for Cofferdam
The height to which a coffer dam should be constructed may involve an economic study of cofferdam height versus diversion works capacity. This may include routing studies of the diversion design flood, especially when the outlet works requirements are small. If the outlet works requirements dictate a relatively large outlet conduit or tunnel, diversion flows ordinarily may be accommodated without a high cofferdam. It should be remembered that the floodwater accumulated behind the cofferdam must be evacuated in time to accommodate another storm.
The maximum height to which it is feasible to construct the cofferdam without encroaching upon the area to be occupied by the dam must also be considered. Furthermore, the design of the cofferdam must take into consideration the effect that excavation and de-watering of the foundation of the dam will have on its stability, and it must anticipate removal, salvage, and other factors.
Coffer Dam Materials
Generally, coffer dams are constructed of materials available at the site. The two types normally used in the construction of dams are
- Earthfill cofferdams and
- Rockfill cofferdams