Definition and Types of Chlorination
Definition:
It is the method of disinfection by which the microorganisms are killed if chlorine & its components are used. Chlorination serves not only for disinfection but as an oxidant for other substances (iron, manganese, cyanide, etc) and for taste & odor control in water & wastewater. Other chemical disinfectants include chlorine dioxide, ozone, bromine, and iodine. The last two chemicals are generally used for personal application, not for the public water supply.
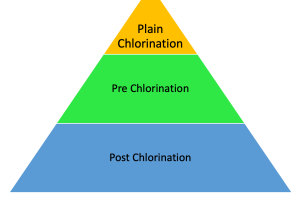
Types of Chlorination
Following are the types of Chlorination:
- Plain Chlorination
- Pre Chlorination
- Post Chlorination
Plain Chlorination
Plain chlorination refers to the process of adding chlorine to water that is relatively free from suspended matter without any other treatment. This method is typically used when the water source is already clear and does not require additional treatment for sediment or particulate removal. The primary purpose of plain chlorination is to disinfect the water by killing or inactivating pathogenic microorganisms present in the water.
Pre Chlorination
Pre-chlorination involves the application of chlorine to raw water before any other treatment processes are conducted. The purpose of pre-chlorination is twofold: first, it helps to improve coagulation by oxidizing certain compounds and facilitating the formation of larger, settleable flocs during the subsequent coagulation and flocculation processes. Second, pre-chlorination helps to remove taste, odor, and color from the water by oxidizing organic compounds responsible for these characteristics.
Post Chlorination
Post-chlorination refers to the application of chlorine to treated water after all other treatment processes have been completed. After the water has undergone coagulation, sedimentation, filtration, and disinfection, post-chlorination provides a final dose of chlorine to maintain a residual disinfectant in the water during distribution. The purpose is to ensure that any remaining microorganisms are destroyed and to provide protection against potential contamination in the distribution system. The dosage of chlorine in post-chlorination is typically in the range of 0.25-5.0 mg/liter to achieve a combined residual chlorine concentration of 0.1-0.2 mg/liter.