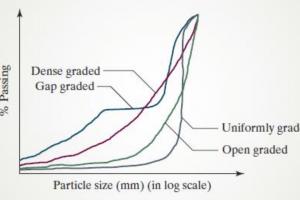
What is a Premix and Types of Premix

Definition:
Something that is mixed or blended from two or more ingredients or elements before being used. This term is used usually for concrete in civil engineering. Premix usually refers to a substance or object that is mixed in an early stage in the manufacturing and distribution process.
Types of premix
- Sheet Asphalt
- Asphalt concrete
- Prime-coat
- Tack-coat
1. Sheet Asphalt
A premix of bitumen and sand (with or without filler) containing coarse aggregate that exceeds 30%, laid in thickness varying from ¾" to ½" (dense carpet, stone metal is discarded and chipping limited to 30%, the rest being sand). Sheet asphalt is a premix that consists of a single layer of asphalt concrete applied directly to the prepared road surface. It is often used for resurfacing existing roads. When an old road surface has deteriorated or become rutted, a new layer of sheet asphalt is applied to rejuvenate the road and improve driving conditions.
- Composition: Sheet asphalt typically consists of a mixture of bitumen (asphalt binder) and aggregates (such as crushed stone or sand) that are heated, mixed, and spread on the road surface.
- Purpose: It is used to provide a smooth, durable, and skid-resistant road surface. Sheet asphalt can help restore the driving quality of worn-out roadways.
2. Asphaltic concrete:
A premix of bitumen and sand (with or without filler) and not less than 30% by weight of mineral aggregate of size larger than sand, mixed and laid at a high temperature around 35 degrees Fahrenheit and required heavy binder generally are 50-60, 60-70, 70-80, 85-100. Asphalt concrete, often referred to as simply "asphalt," is a common road construction material composed of a mixture of bitumen and aggregates. Most highways and major roadways are constructed using asphalt concrete because of its durability and ability to withstand heavy traffic loads.
- Composition: Asphalt concrete typically contains bitumen as the binder and various sizes of aggregates like sand, gravel, and crushed stone.
- Purpose: It is used for constructing road surfaces, including both new road construction and resurfacing existing roads. Asphalt concrete provides a durable, smooth, and skid-resistant driving surface.
3. Prime Coat:
The initial application of binder to an absorbent highway surface prior to the construction of a wearing coat. A prime-coat is a low-viscosity bituminous material applied directly to the prepared road base or subbase before the application of an asphalt layer. Before laying asphalt concrete on a road, a prime-coat is applied to ensure a strong bond between the road base and the asphalt layer.
- Composition: It usually consists of a cutback asphalt or emulsion, which is a bitumen mixed with a solvent or water, respectively.
Purpose of Prime Coat:
- It assists in promoting and maintaining adhesion b/w the road base and the bituminous surfacing. By pre-coating the surface of the road base and wearing coat are glued by penetrating the prime coat in the voids near the surface.
- It helps to bind the finer particles of aggregate together on the surface of the road base.
- If the application of the surface is delayed for some reason it provides the road base of the application against the detrimental effect of rainfall and light traffic.
4. Tack Coat:
The initial application of binder to an existing given surface, to ensure thorough bond b/w the new construction and existing surface. A tack-coat is a thin application of bituminous material applied to the surface of an existing layer of asphalt before a new layer is placed on top. When resurfacing a road, a tack coat is applied over the existing asphalt surface before the new layer of asphalt concrete is placed, ensuring a secure connection between the old and new layers.
- Composition: Tack-coat materials are typically bitumen-based, such as asphalt emulsion or hot-applied asphalt.
- Purpose: Tack-coats enhance the bond between two asphalt layers, promoting a strong and continuous surface. They prevent delamination and slippage between layers.
These various types of premixes play crucial roles in the construction and maintenance of roads, contributing to their durability, smoothness, and overall performance. Proper selection and application of these premixes are essential for creating safe and long-lasting road surfaces.