Airfield Pavement Design

Airfield pavement design forms the foundation of safe and efficient aircraft operations at airports worldwide. From runways to taxiways and aprons, every surface must withstand immense loads and environmental stresses while ensuring smooth movement for aircraft. This article explores the intricacies of airfield pavement design, covering key considerations, materials, thickness design, load-bearing capacity calculations, and maintenance strategies with real-world examples.
Design Considerations for Runways, Taxiways, and Aprons:
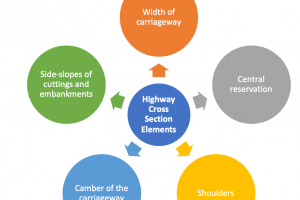
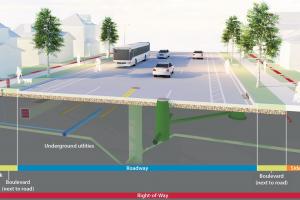
Designing pavements for runways, taxiways, and aprons involves accounting for various factors such as aircraft types, traffic patterns, weather conditions, and expected service life. For instance, at London Heathrow Airport (LHR), runways are designed to accommodate the heavy traffic of wide-body aircraft like the Airbus A380, necessitating robust pavement structures capable of withstanding high wheel loads and frequent aircraft movements.
Materials Used in Airfield Pavement Construction:
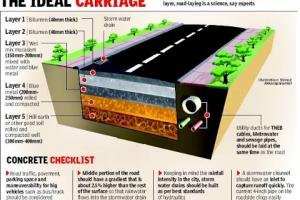
Airfield pavements are typically constructed using durable materials such as concrete, asphalt, or a combination of both. Each material offers distinct advantages based on factors like cost, maintenance requirements, and environmental conditions. For example, Denver International Airport (DEN) utilizes concrete pavements for its runways and taxiways due to their durability and resistance to fuel spills, ensuring long-term performance under heavy aircraft traffic.
Pavement Thickness Design and Analysis:
Determining the appropriate thickness of airfield pavements is crucial for ensuring structural integrity and longevity. Pavement thickness design involves analyzing factors such as aircraft loading, subgrade strength, and pavement material properties. Singapore Changi Airport (SIN) employs sophisticated pavement design methodologies to optimize pavement thicknesses, taking into account varying aircraft loads and traffic patterns to minimize construction costs while ensuring adequate pavement performance.
Load-Bearing Capacity Calculations:
Calculating the load-bearing capacity of airfield pavements is essential for preventing pavement failures and ensuring safe aircraft operations. Load-bearing capacity calculations consider factors such as pavement thickness, material strength, subgrade conditions, and anticipated aircraft loads. Dubai International Airport (DXB) employs advanced pavement analysis techniques to assess load-bearing capacity, enabling informed decision-making in pavement design and maintenance.
Maintenance and Rehabilitation Strategies for Airfield Pavements:
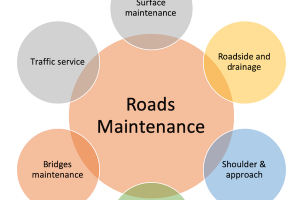
Maintaining and rehabilitating airfield pavements is vital for extending their service life and ensuring continued safe operations. Maintenance strategies include regular inspections, crack sealing, and pavement patching to address surface distresses and prevent deterioration. Additionally, rehabilitation techniques such as asphalt overlays or concrete panel replacement are employed to address structural deficiencies. For instance, Chicago O'Hare International Airport (ORD) implements a proactive pavement maintenance program, utilizing innovative techniques like diamond grinding to restore pavement smoothness and prolong service life.
Airfield pavement design is a complex undertaking that requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure the safe and efficient movement of aircraft. By addressing design considerations, selecting appropriate materials, conducting thorough thickness design and load-bearing capacity calculations, and implementing effective maintenance and rehabilitation strategies, airports can uphold the integrity of their pavements and support continued growth in air travel. As aviation technology advances and air traffic increases, the importance of robust airfield pavement design and management practices will only continue to grow.