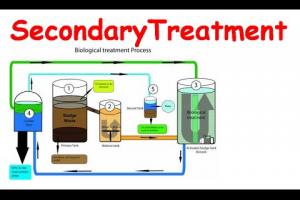
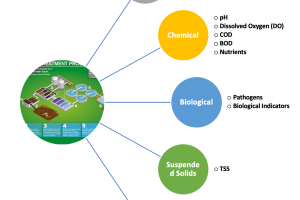
Microbial Metabolism in Biological Waste Water Treatment
Carbon and Energy Sources for Microbial Growth:
- Organism must have sources of energy, carbon for synthesis of new cellular material, and inorganic elements (nutrients) such as nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, potassium, calcium and magnesium;
Carbon Sources:
- Organisms that use organic carbon for formation of new biomass are called heterotrophs; Organisms that derive cell carbon from carbon dioxide are called autotrophs
Energy Sources:
- Energy needed for cell synthesis supplied by light or by chemical oxidation reaction; Those organisms that are able to use light as energy source are called phototrophs; Phototrophic organisms either heterotrophic or autotrophic;
- Organisms that derive energy from chemical reactions are known as chemotrophs; Chemoautotrophs obtain energy from oxidation of reduced inorganic compounds (ammonia, nitrite, ferrous iron and sulfide); Chemoheterotrophs derive their energy from oxidation of organic compounds
- Oxidation‐reduction reactions involve transfer of electrons from electron donor to electron acceptor; Electron donor is oxidized and electron acceptor is reduced; Electron acceptor available within cell during metabolism (endogenous) or it obtained from outside cell (i.e., dissolved oxygen) (exogenous);
Respiratory Metabolism:
- Organisms that generate energy by enzyme‐mediated electron transport to external electron acceptor
Fermentative Metabolism:
Use of internal electron acceptor and is less efficient energy yielding process than respiration
Aerobic:
- When oxygen is used as electron acceptor the reaction is termed aerobic;
Anaerobic:
- When electron acceptors other than oxygen are involved, reaction is considered anaerobic;
Anoxic:
- When nitrite or nitrate is used as electron acceptor, reaction is termed anoxic; Under anoxic conditions nitrite or nitrate reduction to gaseous nitrogen occurs, also referred to as biological denitrification
- Organisms that can only meet their energy needs with oxygen are called obligate aerobes
- Bacteria that can use oxygen or nitrite/nitrate as electron acceptor in absence of oxygen are called facultative aerobes
- Organisms that generate energy by fermentation and that can exist only in environment devoid of oxygen are obligate anaerobes
- Organisms having ability to grow in either presence or absence of oxygen are facultative anaerobes