How to Get a Project Contract
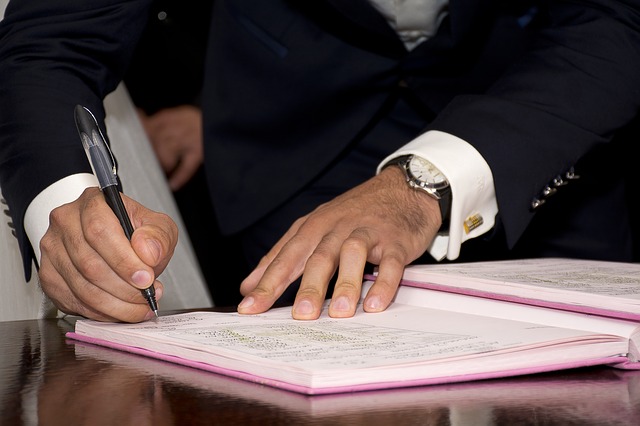

Contract has got a key role in any kind of project i.e. construction, Procurement, Demolishing etc and even in most of the firms there are special persons for it who solely deals in Project contract means how to
- Apply for it
- Compete with other firms
- Win the Contract.
Method of Award
There are three ways in which construction contracts are awarded:
- Competitive awards
- Negotiated awards,
- Combination competitive - negotiated awards

With a purely competitive award, the decision is made solely on the basis of price. The lowest bidder will be awarded the project. Usually, public work is awarded in this manner, and all who meet the minimum qualifications (financial) are allowed to compete. In private work, the competitive method of award is used extensively; however, more care is taken to screen Potential selective bidders.
The term selective bid process describes this method of competitive award. At the opposite extreme from competitive awards are the negotiated awards. In a purely negotiated contract, the contractor is the only party asked to perform the work. Where a price is required prior to initiating work, this price is negotiated between the contractor and the client. Obviously, this lack of competition relieves some of the tension developed in the estimator through the competitive bid process because there is no need to be concerned with the price another contractor might submit. The contractor must still, if asked, provide a firm price that is acceptable to the client and may have to submit evidence of cost or allow an audit.
As the purely competitive and purely negotiated method of contract awards represent the extremes, the combination competitive-negotiated award may fall anywhere in between. A common practice for relatively large jobs is to competitively evaluate the qualifications of several potential constructors and then select and negotiate with a single contractor a price for the work.
Method of Bidding / Payment
Several methods of payment are used to reimburse contractors for the construction services they provide. These methods of payment include lump sum or firm price, unit-price, and cost-plus. Each of these methods of payment requires an appropriate form of bidding that recognizes the unique incentive and risk associated with the method. The requirements for completeness of design and scope definition vary for the various types. The lump-sum or firm-price contract is widely used for well-defined projects with completed designs. This method allows purely competitive bidding. The contractor assumes nearly all of the risk, for quantity and quality. The comparison for bidding is based entirely on the total price submitted by the contractors, and payment for the work is limited to the agreed-upon contract price with some allowance for negotiated changes. The lump sum is the predominant form used for most building projects.
The unit-price contract is employed on highway projects, civil works projects, and pipelines. For these projects, the quality of the work is defined, but the exact quantity is not known at the time of bidding. The price per unit is agreed upon at the time of bidding, but the quantity is determined as work progresses is completed. The contractor, therefore, assumes a risk for quality performance, but the quantity There is a strong tendency, by contractors, to overprice or front-load those bid items that will be accomplished first and compensate with lower pricing on items of work that will be performed later. This allows contractors to improve their cash flow and match their income closer to heir expenses. Each unit-price given must include a portion of the indirect costs and profits that are part of the job. Usually, quantities are specified for bidding purposes so that the prices can be compared or competitive analysis. If contractors