GPS Constellation and Characteristics of GPS Constellation
Global Navigation Satellite System
A Satellite System used to pinpoint a Geographic Location of a user’s receiver anywhere in the world
Two GNSS systems are currently in operation:
- GPS (United States’ Global Positioning System)
- GLONASS (Russian Federation’s Global Orbiting Navigation Satellite System)
Other GNSS under Development:
- Galileo Positioning System (European Union) (2020)
- Compass Navigation System (From Biedou Navigation System) (China)(2020)
Satellite Constellation
A group of artificial satellites working in concert The satellites are:
- Synchronized
- Operate together under shared control
Characteristics of GPS Constellation
Following are some of the characteristics of GPS constellation:
- 24 Satellites
- 6 Orbits
- 4 Satellites per orbit
- Orbit Period = approx 12 hrs
- Orbit Radius = 26600 Km (approx)
- Satellites’ Altitude = 20,200 Km(approx)
- Inclination with Earth = 55 degree
- Angle b/w Orbital Planes = 60 degrees
- Satellites do not rotate w.r.t. Earth but w.r.t distant stars
- 6 to 11 satellites are always in sight from earth surface
- For this purpose the 4 satellites are not evenly spaced (900)
- They are spaced at 30, 105, 120, 105 degrees
- 4 satellites are sufficient for GPS receiver
Working of GPS System (Working Mechanism)
A GPS receiver calculates its position by precisely timing the signals sent by GPS satellites. The receiver uses the messages it receives to determine the transit time of each message and computes the distance to each satellite. The GPS receiver with the help of the satellites determine:
-
Time (t)
-
Longitude(x)
- Latitude(y)
-
Altitude (z)
- Let xi, yi, zi, ti be the x-coordinate, y-coordinate, z-coordinate and time respectively of satellite i
- Let tr be the time the GPS receives the message
- Then the transit time of the message = (tr – ti)
- Assume the message travels at a speed of light c
- Then by distance formula;
- Distance b/w the satellite and GPS receiver = (tr – ti) c
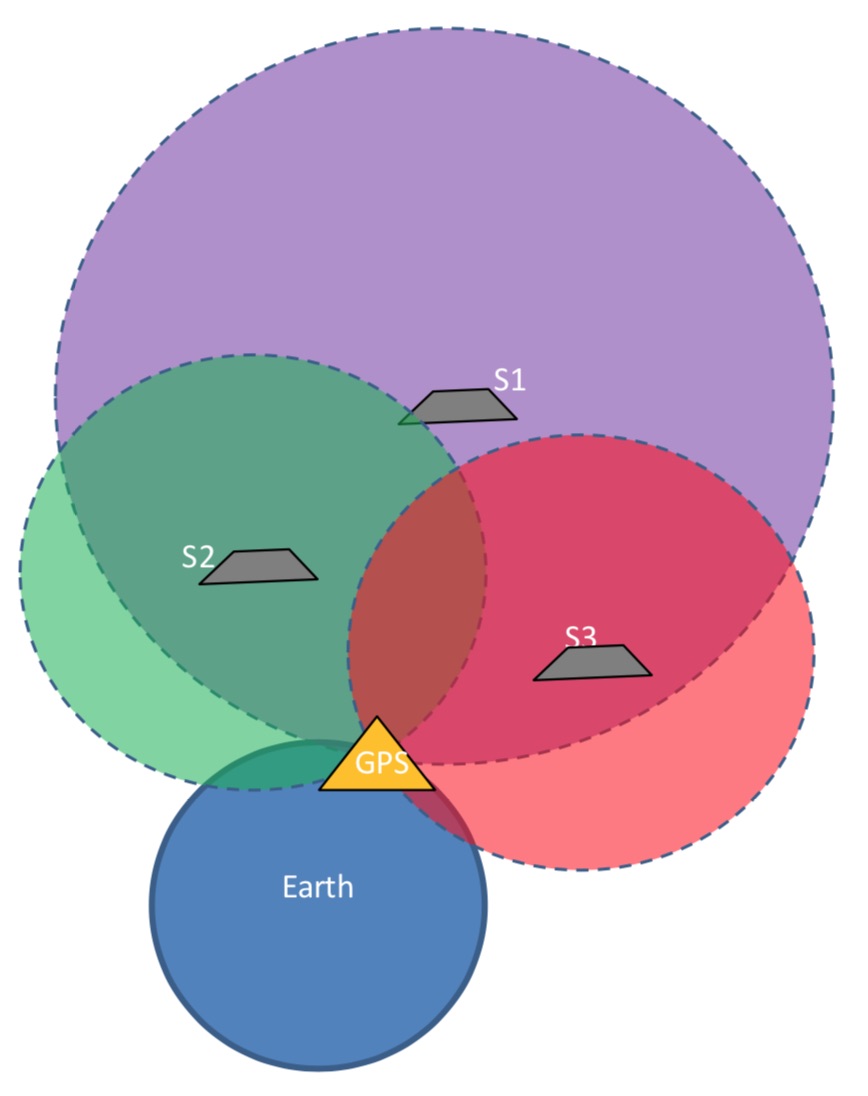
- Consider a receiver receives messages from4 satellites
- Then the position of the receiver is confined by the spheres formed by these 4 satellites
- The center of the sphere is the satellite and the GPS receiver is at its surface, therefore,the distance from the receiver to satellite known as pseudo-range is the radius of the sphere
- The position of the GPS receiver is somewhere at the intersection of these spheres
- Greater the number of spheres smaller will be the intersection space and accurate will be the position of the receiver