Categories of Zoning

Urban Zoning Categories
Zoning categorizes land within a municipality or city into different zones or districts based on specific land use classifications. The exact categories in zoning can vary between jurisdictions, but here are some common categories found in zoning:
Residential Zones:
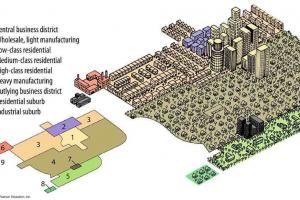
Residential zones are designated for housing purposes and typically include single-family homes, townhouses, apartments, and other residential dwellings. These zones may have subcategories based on housing density, such as low-density residential (R-1), medium-density residential (R-2), and high-density residential (R-3).
Commercial Zones:
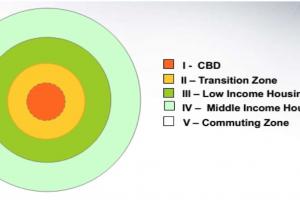
Commercial zones are intended for commercial activities, including retail stores, offices, restaurants, hotels, and other commercial establishments. These zones may have subcategories for different intensities of commercial use, such as neighborhood commercial (C-1), general commercial (C-2), and central business district (CBD).
Industrial Zones:
Industrial zones are designated for manufacturing, warehousing, distribution, and other industrial activities. These zones may have subcategories based on the intensity of industrial use, such as light industrial (I-1), general industrial (I-2), and heavy industrial (I-3).
Mixed-Use Zones:
Mixed-use zones allow for a combination of different land uses within a single zone. These zones promote a mix of residential, commercial, and sometimes industrial or institutional uses to create vibrant and walkable neighborhoods.
Agricultural or Rural Zones:
Agricultural or rural zones are reserved for farming, agricultural activities, and open spaces. These zones may have regulations to protect agricultural land, preserve rural character, and limit non-agricultural development.
Institutional or Public Use Zones:
Institutional or public use zones are designated for public and community facilities, such as schools, hospitals, government offices, libraries, parks, and cultural institutions.
Open Space or Conservation Zones:
Open space or conservation zones are set aside for the preservation of natural areas, parks, forests, wetlands, or environmentally sensitive areas. These zones aim to protect biodiversity, provide recreational opportunities, and maintain ecological balance.
Historic or Preservation Zones:
Historic or preservation zones are designated for the preservation and protection of historically significant buildings, landmarks, or districts. These zones often have strict regulations to maintain the architectural and historical integrity of the area.
Special Purpose Zones:
Special purpose zones cater to unique land uses or specific development requirements that do not fit within the standard zoning categories. Examples include airport zones, waterfront zones, entertainment districts, or research and development zones.
It's important to note that zoning categories can vary across different jurisdictions and may have specific designations and regulations tailored to the local context and planning objectives. The purpose of zoning is to guide land use and development in a manner that promotes orderly growth, protects the welfare of residents, and balances the needs of different stakeholders within a community.